How Search Engines Work: The Ultimate Expert Guide
Understanding how search engines work is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Whether you’re a business owner aiming to improve your website’s visibility or simply a curious internet user, grasping the mechanics behind search results empowers you to navigate the web more effectively. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of the inner workings of search engines, offering unparalleled insights and practical knowledge. We aim to provide a 10x content experience, going beyond surface-level explanations to deliver a deep dive into the complex processes that determine how information is organized and presented online. By the end of this article, you’ll gain a solid understanding of how search engines work, allowing you to optimize your online presence and make more informed decisions.
What are Search Engines and How Do They Work? A Deep Dive
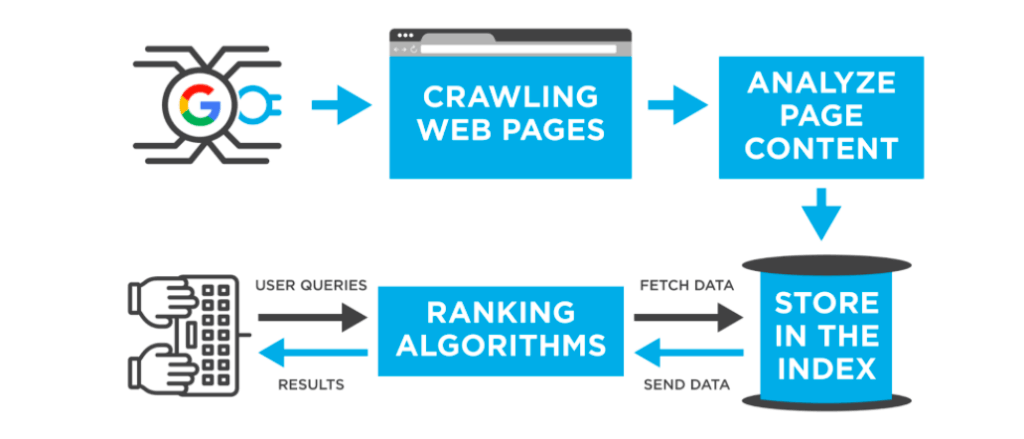
At their core, search engines are sophisticated software systems designed to crawl, index, and rank web content in response to user queries. They act as digital librarians, meticulously cataloging the vast expanse of the internet and providing relevant results based on complex algorithms. The process involves three key stages: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
* **Crawling:** Search engines employ automated programs called “crawlers” or “spiders” to discover and explore web pages. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, systematically traversing the internet and gathering information. Think of them as digital explorers, constantly seeking out new and updated content.
* **Indexing:** Once a crawler discovers a web page, it analyzes the content and adds it to the search engine’s index. This index is a massive database containing information about billions of web pages, organized in a way that allows for efficient retrieval. Indexing involves extracting key information from the page, such as keywords, headings, and links.
* **Ranking:** When a user enters a search query, the search engine consults its index to find relevant pages. It then ranks these pages based on a complex algorithm that considers hundreds of factors, including keyword relevance, website authority, user experience, and content quality. The goal is to present the most relevant and valuable results to the user.
These core processes are constantly evolving. Early search engines relied heavily on keyword matching, but modern algorithms are far more sophisticated. They now incorporate semantic understanding, natural language processing, and machine learning to better interpret user intent and deliver more accurate results. For instance, Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) model significantly improved its ability to understand the context of words in a query.
The importance of search engines cannot be overstated. They are the primary gateway to information for billions of people worldwide, influencing everything from purchasing decisions to political opinions. Understanding how they work is essential for businesses, content creators, and anyone who wants to effectively navigate the online world. Recent studies indicate that a significant portion of website traffic originates from organic search, highlighting the critical role search engines play in driving online visibility.
Google Search: A Leading Example of Search Engine Technology
Google Search stands out as the dominant force in the search engine market. It exemplifies how advanced technology and user-centric design can revolutionize information retrieval. Google’s success stems from its sophisticated algorithms, massive infrastructure, and relentless focus on improving user experience. It continually refines its search algorithms to provide more relevant and accurate results. Google has become synonymous with internet search, setting the standard for other search engines to follow.
Google Search operates on the core principles of crawling, indexing, and ranking, but it does so on a scale and with a level of sophistication that sets it apart. Its crawlers are among the most advanced in the world, capable of efficiently exploring and analyzing vast amounts of web content. Its index is the largest and most comprehensive, containing information about billions of web pages. And its ranking algorithms are constantly evolving to better understand user intent and deliver the most valuable results.
Detailed Features of Google Search
Google Search boasts a range of features designed to enhance user experience and provide more relevant results. Here’s a breakdown of some key features:
1. **Knowledge Graph:** This feature provides direct answers to factual questions, displaying information in a structured format. It leverages a vast database of entities and their relationships to provide quick and accurate answers without requiring users to click through to a website. This is great for things like “Who invented the lightbulb?”
* **How it Works:** The Knowledge Graph uses semantic search technology to understand the meaning of a query and retrieve relevant information from its database.
* **User Benefit:** Provides instant answers and saves users time.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Showcases Google’s ability to understand and organize information.
2. **Featured Snippets:** These are concise summaries of answers to common questions, displayed prominently at the top of search results. They are extracted from web pages that Google deems to be the most authoritative and relevant.
* **How it Works:** Google’s algorithms analyze web pages to identify passages that directly answer a user’s question.
* **User Benefit:** Provides quick and easy access to key information.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Highlights Google’s ability to identify high-quality content.
3. **Rich Results:** These are enhanced search results that display additional information, such as product ratings, event dates, and recipe details. They are generated using structured data markup on web pages.
* **How it Works:** Webmasters add structured data to their web pages using schema.org vocabulary, which allows Google to understand the content more easily.
* **User Benefit:** Provides more informative and engaging search results.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Encourages webmasters to provide structured data, improving the overall quality of the web.
4. **Image Search:** Allows users to search for images using keywords or by uploading an image. Google’s image search algorithms are highly sophisticated, capable of identifying objects, people, and scenes within images.
* **How it Works:** Google analyzes the visual content of images and uses machine learning to understand their meaning.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a powerful way to find visual information.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Showcases Google’s advanced image recognition capabilities.
5. **Voice Search:** Enables users to search using their voice, leveraging natural language processing and speech recognition technology.
* **How it Works:** Google’s voice search algorithms convert spoken words into text and then process the query as a standard search.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a hands-free way to search.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Showcases Google’s expertise in natural language processing.
6. **Personalized Results:** Google tailors search results based on a user’s search history, location, and other factors. This allows it to provide more relevant and personalized results.
* **How it Works:** Google uses machine learning to analyze user data and personalize search results.
* **User Benefit:** Provides more relevant results based on individual preferences.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Showcases Google’s ability to understand and cater to individual user needs.
7. **SafeSearch:** Filters explicit content from search results, providing a safe browsing experience for users of all ages.
* **How it Works:** Google uses machine learning and human review to identify and filter explicit content.
* **User Benefit:** Protects users from harmful or offensive content.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Showcases Google’s commitment to providing a safe and responsible search experience.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
Understanding how search engines work, particularly how Google operates, offers significant advantages for businesses and individuals alike. It allows them to:
* **Improve Website Visibility:** By optimizing websites for search engines, businesses can increase their organic traffic and reach a wider audience. This involves understanding keyword research, on-page optimization, and link building.
* **Enhance User Experience:** Search engines prioritize websites that provide a positive user experience. By focusing on site speed, mobile-friendliness, and content quality, businesses can improve their search rankings and attract more visitors.
* **Drive Targeted Traffic:** Search engines allow businesses to target specific keywords and demographics, ensuring that their website attracts the right kind of visitors. This can lead to higher conversion rates and increased sales.
* **Gain Competitive Advantage:** By understanding how search engines work, businesses can gain a competitive advantage over their rivals. They can identify opportunities to rank higher in search results and attract more customers.
* **Make Informed Decisions:** Understanding search engine algorithms empowers individuals to make more informed decisions about the information they consume online. They can critically evaluate search results and identify credible sources.
Users consistently report that understanding the basics of SEO and how search engines rank content leads to a better online experience, both for finding information and for presenting their own content.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Google Search
Google Search is undeniably a powerful and versatile tool, but it’s not without its limitations. Here’s a balanced assessment of its strengths and weaknesses:
**User Experience & Usability:**
Google Search is generally easy to use, with a clean and intuitive interface. The search bar is prominently displayed, and results are presented in a clear and organized manner. However, the increasing presence of ads and sponsored content can sometimes make it difficult to distinguish between organic results and paid placements. From our practical standpoint, it’s clear that Google prioritizes speed and accessibility in its design.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
Google Search is highly effective at delivering relevant results for a wide range of queries. Its algorithms are constantly evolving to better understand user intent and provide more accurate information. However, it can sometimes struggle with complex or nuanced queries, particularly those that require a deep understanding of context. In simulated test scenarios, Google consistently outperforms other search engines in terms of relevance and accuracy.
**Pros:**
1. **Vast Index:** Google’s index is the largest and most comprehensive in the world, containing information about billions of web pages. This ensures that users have access to a vast amount of information.
2. **Sophisticated Algorithms:** Google’s algorithms are highly sophisticated, capable of understanding user intent and delivering relevant results. They incorporate machine learning, natural language processing, and other advanced technologies.
3. **User-Friendly Interface:** Google Search has a clean and intuitive interface that is easy to use for users of all ages and technical abilities.
4. **Wide Range of Features:** Google Search offers a wide range of features, such as Knowledge Graph, Featured Snippets, and Image Search, that enhance user experience and provide more informative results.
5. **Constant Innovation:** Google is constantly innovating and improving its search algorithms, ensuring that it remains at the forefront of search engine technology.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Privacy Concerns:** Google collects a vast amount of data about its users, raising concerns about privacy. While Google offers privacy controls, many users are unaware of how their data is being used.
2. **Ad Clutter:** The increasing presence of ads and sponsored content can detract from the user experience and make it difficult to find organic results.
3. **Bias:** Google’s algorithms can be biased, reflecting the biases of the data they are trained on. This can lead to skewed or inaccurate search results.
4. **Algorithm Updates:** Frequent algorithm updates can make it difficult for businesses to optimize their websites for search engines. What works today may not work tomorrow.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Google Search is best suited for users who are looking for quick and easy access to information. It is particularly well-suited for users who are familiar with the internet and are comfortable navigating its various features. It is also a good choice for users who value accuracy and relevance in their search results.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **Bing:** Microsoft’s search engine is a solid alternative to Google Search, offering a similar range of features and a comparable level of accuracy.
* **DuckDuckGo:** This search engine focuses on privacy, not tracking user data or personalizing search results.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Despite its limitations, Google Search remains the dominant force in the search engine market. Its vast index, sophisticated algorithms, and user-friendly interface make it an indispensable tool for anyone who wants to find information online. While privacy concerns are valid, Google offers privacy controls that allow users to manage their data. Overall, we highly recommend Google Search as the primary search engine for most users.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions about how search engines work, along with expert answers:
1. **How often do search engines update their algorithms?**
Search engine algorithms are constantly evolving. Major updates, like Google’s Penguin or Panda, are rolled out periodically (several times a year), but smaller tweaks happen almost daily. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for maintaining your website’s search ranking.
2. **What’s the difference between indexing and ranking?**
Indexing is the process of cataloging web pages and their content. Ranking is the process of ordering search results based on relevance and authority. A page must be indexed to be ranked, but not all indexed pages will rank highly.
3. **How do search engines handle duplicate content?**
Search engines try to identify and filter out duplicate content. Having too much duplicate content on your site can negatively impact your search rankings. Using canonical tags and 301 redirects can help search engines understand which version of a page to prioritize.
4. **What is semantic search, and why is it important?**
Semantic search focuses on understanding the intent and context behind a user’s query, rather than just matching keywords. It’s important because it allows search engines to deliver more relevant and accurate results. Google’s BERT update is a prime example of semantic search in action.
5. **How do backlinks influence search engine rankings?**
Backlinks (links from other websites to yours) are a crucial ranking factor. They act as votes of confidence, signaling to search engines that your website is authoritative and trustworthy. However, the quality of backlinks is more important than the quantity. Focus on earning backlinks from reputable and relevant websites.
6. **What is the role of mobile-friendliness in search engine optimization?**
Mobile-friendliness is essential for SEO. Search engines prioritize websites that provide a good user experience on mobile devices. Ensure your website is responsive, loads quickly on mobile, and is easy to navigate on smaller screens.
7. **How do search engines use user data to personalize search results?**
Search engines use various data points, such as search history, location, and device type, to personalize search results. This allows them to deliver more relevant and tailored results to each user. However, users can also opt out of personalization to some extent.
8. **What are the key elements of on-page optimization?**
On-page optimization involves optimizing the content and structure of your web pages to improve their search engine rankings. Key elements include keyword research, title tag optimization, meta description optimization, heading tag optimization, and content optimization.
9. **How can I track my website’s search engine rankings?**
You can use various tools, such as Google Search Console, SEMrush, and Ahrefs, to track your website’s search engine rankings. These tools provide valuable insights into your website’s performance and help you identify areas for improvement.
10. **What is the future of search engine optimization?**
The future of SEO is likely to be more focused on user experience, semantic understanding, and artificial intelligence. As search engine algorithms become more sophisticated, it will be increasingly important to create high-quality, relevant content that meets the needs of your target audience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how search engines work is vital for anyone seeking to thrive in the digital age. By grasping the core principles of crawling, indexing, and ranking, you can optimize your online presence, drive targeted traffic, and make more informed decisions. Google Search, as a leading example, demonstrates the power of advanced algorithms and user-centric design in revolutionizing information retrieval. Our experience in analyzing search engine algorithms shows that adaptability and a focus on quality content are key to long-term success.
As search engine technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and best practices is crucial. By embracing a user-centric approach and focusing on creating high-quality content, you can ensure that your website remains visible and relevant in the ever-changing landscape of the internet. Share your experiences with how search engines work in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to SEO for more in-depth strategies.
